C break statement
The break statement in C language is used to break the execution of loop (while, do while and for) and switch case.
In case of inner loops, it terminates the control of inner loop only.
There can be two usage of C break keyword:
- With switch case
- With loop
Syntax:
The jump statement in c break syntax can be while loop, do while loop, for loop or switch case.
Flowchart of break in c
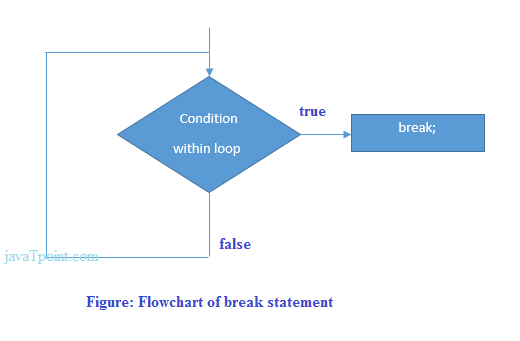
Example of C break statement with switch case
Click here to see the example of C break with switch statement.
Example of C break statement with loop
Output
1 2 3 4 5
As you can see on console output, loop from 1 to 10 is not printed after i==5.
C break statement with inner loop
In such case, it breaks only inner loop, but not outer loop.
Output
1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 3 3
As you can see the output on console, 2 3 is not printed because there is break statement after printing i==2 and j==2. But 3 1, 3 2 and 3 3 is printed because break statement works for inner loop only.
No comments:
Post a Comment